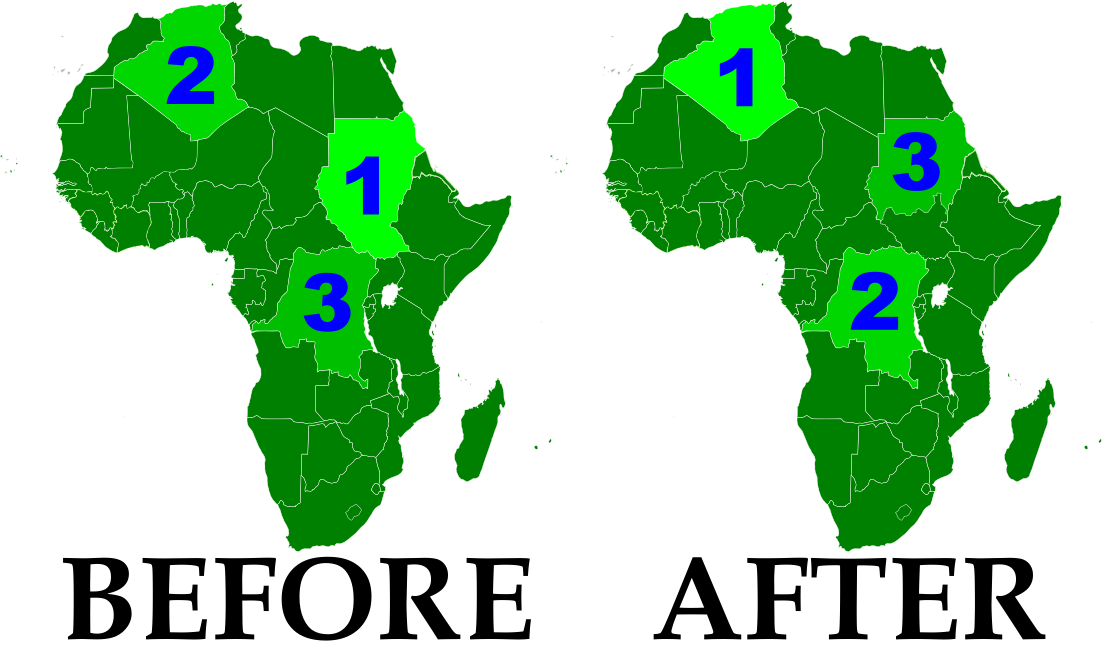
What Is Africa's Largest Country?
Africa, the second-largest continent in the world, is home to a diverse range of countries, cultures, and landscapes. Among them, one country stands out as the largest in terms of land area, sparking curiosity and a wealth of interesting facts. Understanding which country holds this title can provide insights into Africa's geography, demographics, and cultural significance. In this article, we will explore the largest country in Africa, its characteristics, and its role on the continent.
With its vast expanse, the largest country in Africa offers stunning landscapes, rich resources, and a population that reflects the continent's diversity. This article will delve into various aspects of this remarkable nation, including its geography, history, and significance within Africa. You'll gain a better understanding of what makes this country unique and why it holds the title of the largest in Africa.
As we journey through this topic, we aim to provide you with well-researched information that adheres to principles of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. By the end of this article, you will not only know which country is the largest in Africa but also appreciate its impact on the continent and the world.
Table of Contents
- 1. The Largest Country in Africa
- 2. Geography of the Largest Country
- 3. Historical Background
- 4. Demographics and Population
- 5. Economy and Resources
- 6. Cultural Diversity
- 7. Political Landscape
- 8. Conclusion
1. The Largest Country in Africa
The largest country in Africa is Algeria. Covering an area of approximately 2.38 million square kilometers (919,595 square miles), Algeria is located in North Africa and is bordered by Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Western Sahara, and Morocco. The Mediterranean Sea lies to the north of the country, providing it with a coastline of about 1,600 kilometers (994 miles).
Algeria's vast size makes it the tenth-largest country in the world, which is a remarkable feat considering Africa's diverse geography and ecosystems. The country is characterized by its varied landscapes, including the Sahara Desert, mountainous regions, and fertile coastal plains.
Key Facts About Algeria
- Capital: Algiers
- Official Language: Arabic and Berber
- Population: Approximately 44 million (as of 2021)
- Currency: Algerian Dinar (DZD)
2. Geography of the Largest Country
Algeria's geography is a stunning mix of deserts, mountains, and coastal regions. The Sahara Desert occupies a significant portion of the country, making it one of the most arid regions in the world. However, Algeria also boasts the Atlas Mountains, which provide a stark contrast to the vast desert landscapes.
The Mediterranean coastline is another highlight, featuring beautiful beaches and a climate that attracts tourists from around the world. Algeria's geography not only influences its climate but also its agriculture, economy, and population distribution.
3. Historical Background
Algeria has a rich and complex history that dates back to ancient times. The region has been inhabited since prehistoric times and has witnessed the rise and fall of several civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Romans, and Byzantines. The country was also part of the Islamic empires that spread across North Africa.
In the 19th century, Algeria became a French colony, leading to a long and brutal struggle for independence. The Algerian War of Independence, which lasted from 1954 to 1962, resulted in significant loss of life and ultimately led to Algeria gaining independence from France in 1962. This history has shaped Algeria's national identity and continues to influence its politics and society today.
4. Demographics and Population
Algeria's population is diverse, consisting of various ethnic groups, with the majority being Arab-Berber. The country has a young population, with a median age of around 28 years. Urbanization has been on the rise, with major cities like Algiers, Oran, and Constantine serving as cultural and economic hubs.
The population is also characterized by a significant youth demographic, with a high percentage of the population being under 30 years old. This demographic trend presents both opportunities and challenges for the country in terms of education, employment, and social services.
5. Economy and Resources
Algeria's economy is heavily reliant on hydrocarbons, with oil and natural gas accounting for the majority of its revenue. The country is one of the largest producers of natural gas in Africa and is a member of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). This reliance on oil and gas has made Algeria vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy prices.
In recent years, the government has sought to diversify the economy by promoting sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy. However, the economy still faces challenges, including high unemployment rates and economic disparities between urban and rural areas.
6. Cultural Diversity
Algeria is known for its rich cultural heritage, which is a blend of Arab, Berber, and French influences. The country celebrates a variety of cultural traditions, including music, dance, and art. The Mediterranean influences are evident in Algerian cuisine, which features a mix of spices, grains, and fresh ingredients.
Festivals and cultural events play a significant role in Algerian society, with celebrations such as the Amazigh New Year and various music festivals showcasing the country's vibrant cultural landscape. The preservation of Berber culture and language has also gained attention in recent years, reflecting the country's commitment to honoring its diverse heritage.
7. Political Landscape
Algeria operates as a presidential republic, with a political system characterized by a strong executive branch. The country has experienced periods of political unrest and instability, particularly during the Arab Spring in 2011 and the subsequent protests in 2019 that led to the resignation of long-time president Abdelaziz Bouteflika.
In recent years, Algeria has been working towards political reform and greater civic engagement, with an emphasis on addressing the demands of its youth population. The political landscape continues to evolve, and the future of Algeria's governance remains a topic of interest for both citizens and international observers.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, Algeria stands as Africa's largest country, boasting a rich history, diverse geography, and a vibrant culture. Understanding Algeria's significance on the continent provides valuable insights into the complexities of African nations and their roles in the global arena. From its vast deserts to its bustling cities, Algeria represents a unique blend of tradition and modernity.
We encourage you to share your thoughts about Algeria in the comments below or explore our other articles for more insights into the fascinating countries of Africa.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more engaging content!
What Sign Is Blueface? Discovering The Zodiac Sign Of The Rapper
David Sutcliffe Net Worth: An In-Depth Analysis Of His Wealth And Career
Uplifting Good Morning Wednesday Inspirational Quotes